X-ray Computed Tomography Analyses
Discover what can be extracted and quantified from X‑ray CT images.
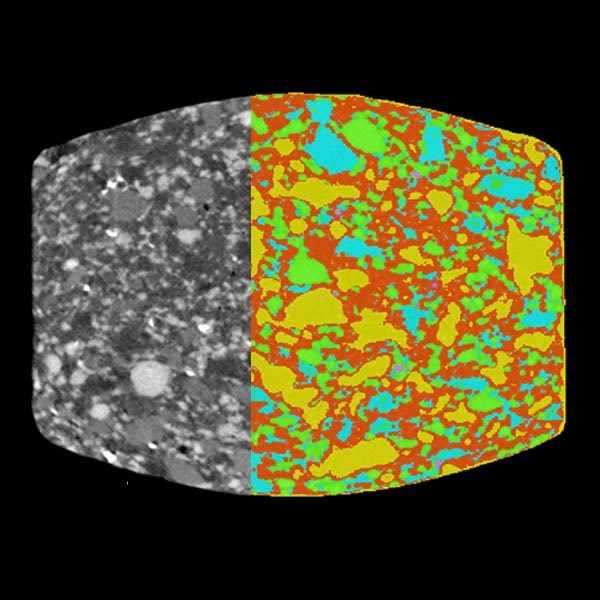
Phase volume fraction analysis
X-ray CT (computed tomography) can differentiate phases or materials that have different densities. They show up with different gray levels in the CT image, normally a lighter shade representing a higher density. The grayscale CT images can be segmented into different phases, and the volume fraction of each phase can be calculated based on how many voxels are in that phase.
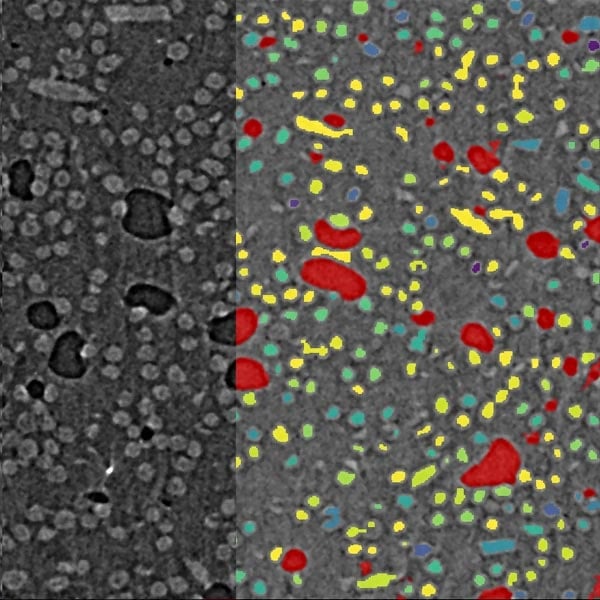
Particle, pore, and fiber analysis
Particles, pores, and fibers can be imaged using X‑ray CT. Their size, shape, etc., can be quantified once they are segmented and separated as individual objects. For fibers, their orientation, length, and aspect ratio can be analyzed. Pores or void space can be converted into a pore network (pores and throats) for pore network analysis, such as connectivity analysis, tortuosity analysis, and permeability simulation.
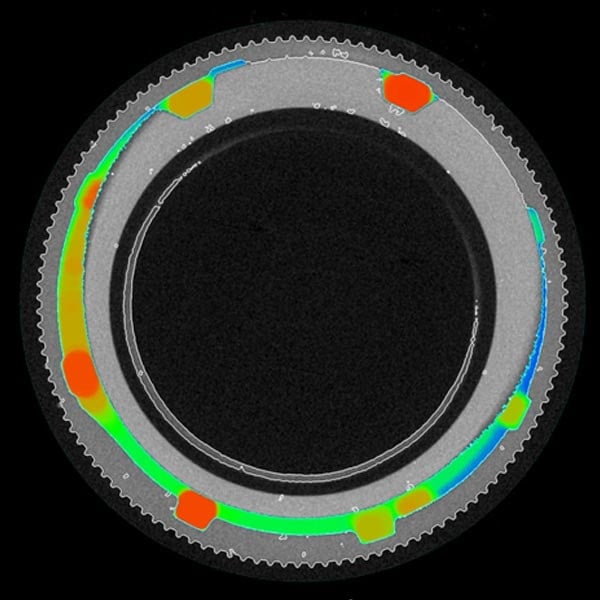
Coating and wall thickness analysis
Coatings, cell walls, and internal structures, such as support grids in 3D printed parts, can be imaged using X-ray CT. Once they are segmented and converted into a surface mesh, the wall thickness distribution can be analyzed and visualized in a color-coordinated manner.
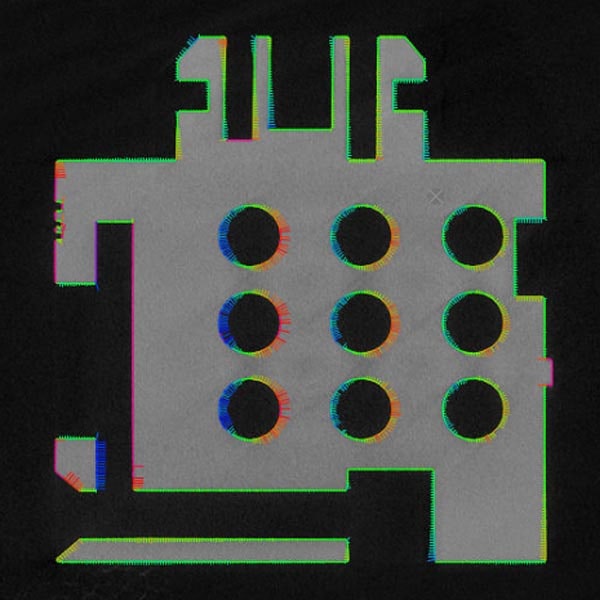
Metrology and dimensional analysis
X‑ray CT can scan the entire volume of various parts in 3D, allowing the analysis of external and internal dimensions. This technique can be used for dimensional analysis, including nominal versus actual comparison, GD&T (Geometric dimensional and tolerancing) analysis, and is becoming a more commonly used testing tool as additive manufacturing technology (a.k.a. 3D printers) makes complex internal structures easy to manufacture. For dimensional analyses, it is important to run scale calibration measurements and determine the object surface correctly in the image analysis.
Non-destructive 3D imaging
X‑ray CT is a non-destructive three-dimensional imaging technique. It can be used to see objects in 3D for various reasons. Examples include failure analysis of mechanical parts, circuit boards, metal and plastic devices, etc. X‑ray CT is also used to see the interior of drug tablets to evaluate the grain size and mixture uniformity or check for cracks, voids, or degradation.
Learn more CT data analyses
As powerful as micro-CT is, the quantitative analysis of the obtained CT images can be challenging. Watch webinars about how to analyze CT data and how various analysis techniques are applied to different types of samples. Or, if you prefer to read, you might like this comprehensive guide, "What is micro CT."


Contact Us
Whether you're interested in getting a quote, want a demo, need technical support, or simply have a question, we're here to help.

Subscribe to the X-ray CT Email Updates newsletter
Stay up to date with CT news and upcoming events and never miss an opportunity to learn new analysis techniques and improve your skills.
