Background
Referencing "Clays and Clay Minerals", a paper by Daniel B. Shaw, "commercially mined clays are added to drilling fluids to build viscosity, control fluid loss, etc." Additionally, "one or more clay minerals are present in nearly all sedimentary rocks and their reaction to the drilling process can produce major problems, such as hole enlargement, sloughing, shale hydration and the gumbo phenomenon." These clay minerals "are also the most unstable minerals. Their composition and structure determine their properties, which to a large extent govern the properties of rocks in which they occur. Therefore, it is important to understand these minerals in order to assess and predict potential drilling problems."
Investigation
Rigaku's ZSX Primus II WDXRF spectrometer was used to analyze geological samples in support of the X-ray diffraction analysis being performed.


The sample, a piece of shale placed along side a piece of slate, was simply surfaced to present a flat sample area, loaded into a mapping sample cup (Figures 1 and 2) and otherwise analyzed as-is on the Rigaku ZSX Primus using the very simple EZ Scan semi-quantitative analysis routine in conjunction with the small-spot/mapping capabilities of the Rigaku ZSX Primus.
|
|
(Slate-SQX) |
(Shale-SQX) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
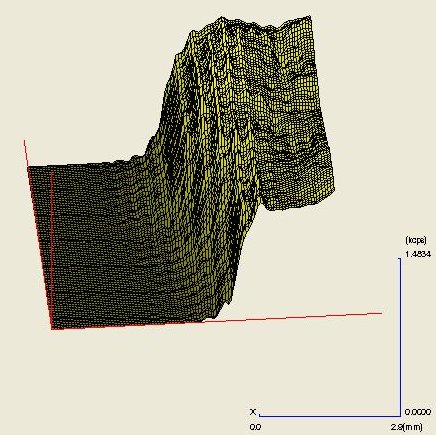
From the 1 mm diameter spot analyses of the shale and slate regions (Table 1), the softer shale appears quite different from the harder, more stable slate, and those differences are dramatically visualized in the 3-dimensional elemental maps. (See elemental maps)
Al:
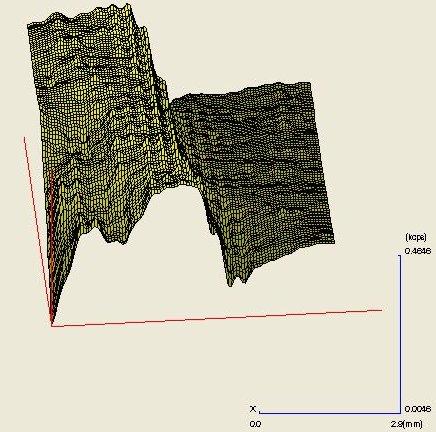
Ca:
The presence of potassium may indicate the presence of alkali feldspars, but the presence of calcium and sodium may indicate the presence of non-swelling and swelling clays, respectively. Montmorillionite, bentonite, or smectite are generic terms for these clays.
Fe:

K:
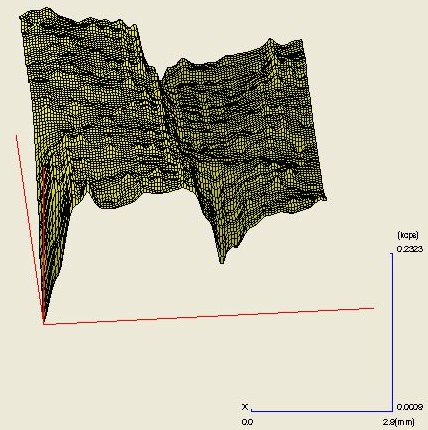
As a side note, high end roofing and flooring installations utilize slate because of it's durability and ability to withstand exposure to wet weather. In construction, shale would be a poor substitute for slate, though cheaper, except in less demanding applications.
Na:

S:
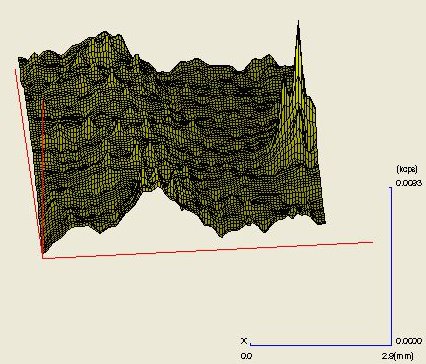
The Rigaku ZSX Primus is a 4KW WDXRF system that offers mapping and small spot (down to 0.5 mm) analysis. Combined with an analytical range from F - U it provides the geologist opportunities to look directly at rocks or petrographic plates. The XRF data thus acquired is quite useful in providing supporting elemental information to help understand x-ray powder diffraction data.
Si:

The powder X-ray diffraction technique can be used to determine whether a sample is shale or slate. Please see the application byte Shale vs. slate XRD identification—know your slate or pay dearly for details.
