Application Note B-TA1020
Introduction
Differential scanning calorimetry or DSC is a thermal analysis technique that measures the temperature and energy changes due to endothermic or exothermic reactions that occur as a sample is heated or cooled. It is used in a wide application range of materials such as polymers, pharmaceuticals, biomaterials and food. In edible oils, the DSC result is significantly influenced by the fatty acids (FA) and triacylglyerols (TAG); and serves a fingerprint profile of a material. In this application, DSC is used in the characterization of fresh extra virgin olive oil (EVOO).
Measurements and results
A 6 mg fresh sample of EVOO was placed in a seal Al pan. DSC measurements were performed from -70℃ up to 30℃ cooling at 5℃/min and heating at 2℃/min in N₂ atmosphere flowing at 50 ml/min. The heating (black) and cooling (blue) DSC curves of fresh EVOO are reported in Figure 1.
The cooling curve reveals two exothermic peaks at -42℃ due to the crystallization of TAG including an oleic moiety and triolein and at -14℃ which is related to the crystallization of monosaturated TAG and disaturated TAG. On the other hand, the heating curve shows three behaviors, an exothermic peak at -21℃ which is immediately followed by two endothermic peaks at -7℃ which is due to the melting of TAG and melting of monosaturated TAG and disaturated TAG at 5℃. The exothermic phenomena observed on the heating curve is due to the rearrangement of metastable crystals into a more thermodynamically stable form.
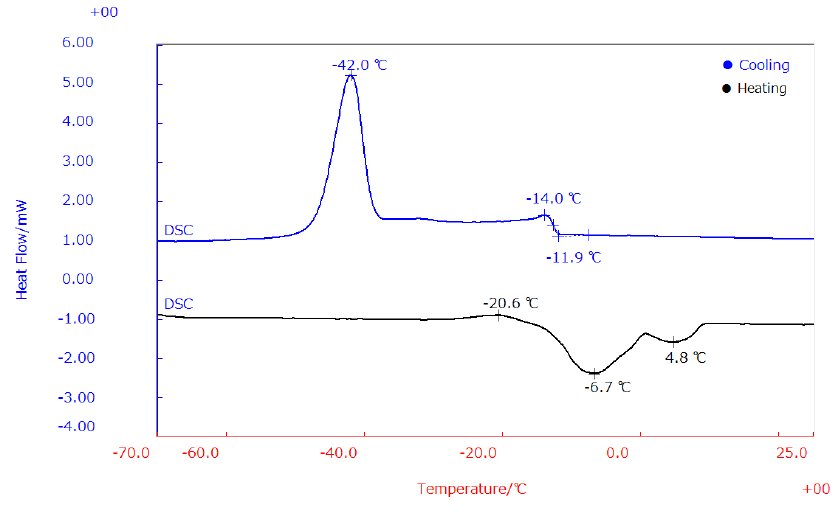
Figure 1: Cooling and heating curves of EVOO by DSC
Reference
(1) S.V. Ciprioti, M. Paciulli and E. Chiavaro. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 118 (2016) 1-16

