Non-destructive 3D Imaging
X-ray CT (computed tomography) is a non-destructive 3D imaging technique. Because of its non-destructive nature, it has been used to image the brains and organs of humans and animals. This technique can also be used to image various things, such as mechanical parts, electronic parts, rocks, fossils, food, etc.
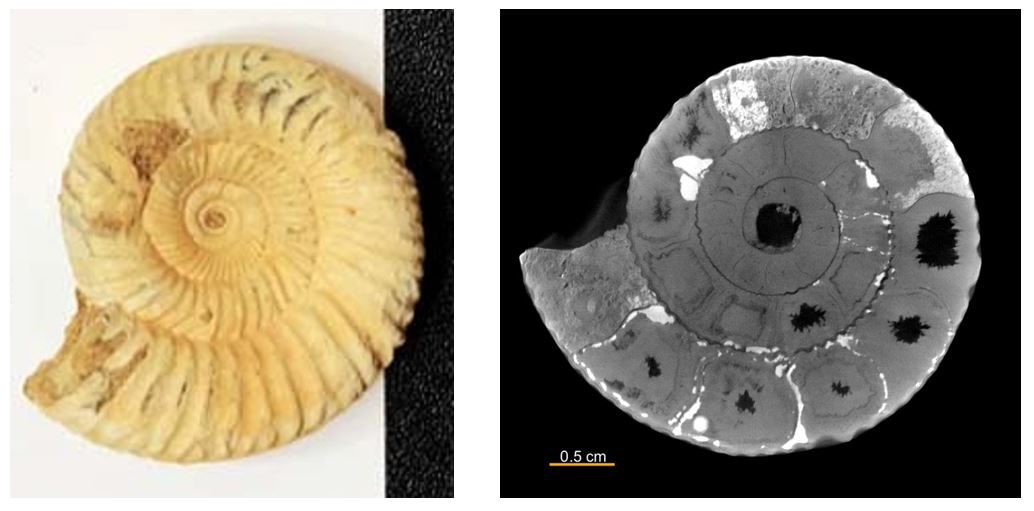
How does it work?
Analysis procedure
The non-destructive 3D imaging involves the following steps:
- Obtain a CT scan of the object.
- The CT images are usually segmented into different materials distinguished by their different X‑ray transparency.
- The object's internal structure details are studied by highlighting or hiding different materials.
- Characteristics, such as volume fraction or pore size distribution, can also be analyzed.
Learning resources
To learn more about general image segmentation:
To learn about CT's application to archaeological and ethnographic ceramics:
To learn more about X‑ray micro-CT:
Non-destructive 3D imaging application examples
Explore application examples to see if this technique can help you with your research or production challenges.
What is micro-CT?
How does it work? How much does it cost? Do I need It? What are the common problems?
To learn everything you need to know about micro-CT, you can start here: What is micro-CT?

Contact Us
Whether you're interested in getting a quote, want a demo, need technical support, or simply have a question, we're here to help.

Subscribe to the X-ray CT Email Updates newsletter
Stay up to date with CT news and upcoming events and never miss an opportunity to learn new analysis techniques and improve your skills.
